explorationsmachiningof the core world. This article details the principles, characteristics and application scenarios of traditional machining processes such as turning, milling, drilling and grinding to help you choose the most appropriate machining method for your project.
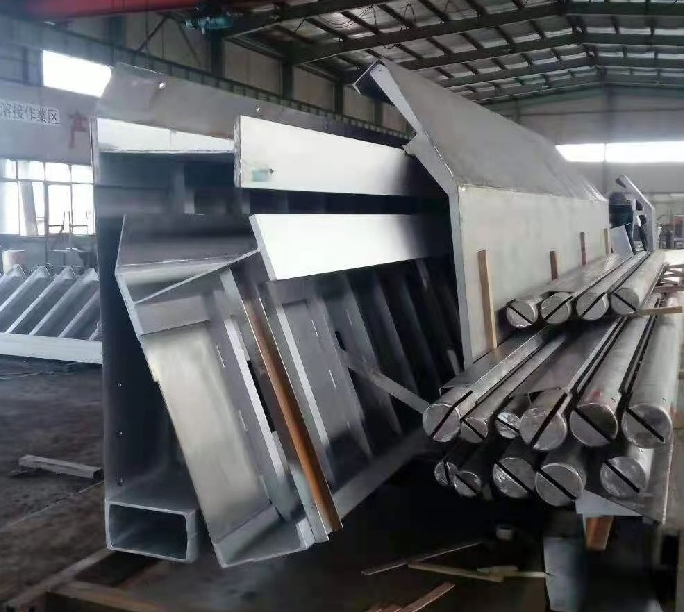
Machining, the cornerstone of manufacturing, is the process of removing excess material from a workpiece (e.g., metal, plastic, wood) by mechanical force, using a cutting tool, in order to obtain a predetermined shape, dimensions, and surface accuracy. It is the foundation of all mechanical manufacturing and maintenance.![图片[1]-机加工基础知识全面解析:从传统工艺到现代应用-大连富泓机械有限公司](https://cndlfh.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/11/QQ20251102-193551.png)
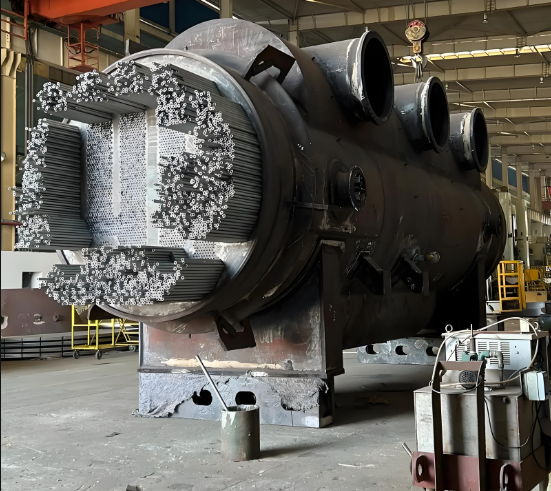
Despite the rapid changes in modern technology, the following traditional machining methods are still the backbone of the workshop: Turning Principle: The workpiece is rotated and the cutting tool moves along a fixed path to cut. Main equipment: lathe. Application: Mainly used for machining shafts, discs, sleeves and other rotating body parts, can be external, internal holes, threads, end faces and other operations. Milling Principle: The tool rotates, the workpiece is fixed to the table and moves, and the material is removed by the rotary motion of the multi-flute tool. Main equipment: Milling machine. Application: Machining of flat surfaces, grooves, gears, complex curved surfaces, etc. It is one of the most widely used machining methods because of its high flexibility. Drilling Principle: Machining of round holes in solid material using specialised rotary tools (drills). Main equipment: Drilling machine. Application: Almost all parts requiring holes cannot be produced without drilling, which is the basic hole processing method. Grinding Principle: The use of a high-speed rotating grinding wheel (made of abrasive grains bonded together) to make minute cuts on the surface of a workpiece. Main equipment: Grinding machine. Application: Mainly used for finish machining to obtain very high dimensional accuracy and excellent surface finish, often used for hard parts after heat treatment.![图片[2]-机加工基础知识全面解析:从传统工艺到现代应用-大连富泓机械有限公司](https://cndlfh.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/10/QQ20251002-201517-1.png)
Second, how to choose the right machining process? The choice of which process depends on a number of factors: part geometry: rotary body priority turning, plane and complex contours consider milling. Material type: different materials need to match different materials and cutting parameters of the tool. Precision and finish requirements: turning and milling for general precision, and grinding for high precision. Production cost and efficiency: the batch size directly affects the process selection and fixture design.
Summary: Understanding these basic machining processes is a prerequisite for product design, manufacturing and outsourcing. They are a critical bridge to get from the drawing board to the physical object, and their foundational position remains unshakeable even in today's highly automated world.











No comments