explorationsmachiningThe world! This article in-depth analysis of turning, milling, drilling, boring, grinding, wire cutting, laser machining 7 mainstream ways, a detailed comparison of its processing characteristics, precision, applicable materials, to help you choose the best process for the project.
![图片[1]-机加工有哪些加工方式和特点?7大主流工艺全解析与选型指南-大连富泓机械有限公司](https://cndlfh.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/12/QQ20251102-193858.png)
Panorama of machining methods: in-depth analysis of features and practical selection
INTRODUCTION: “Understanding a machine shop is the first step, getting to the heart of its core technology is the only way to communicate effectively. Different part characteristics require different machining methods.”
I. Basis of classification: rotational vs. non-rotational, contact vs. non-contact
II. 7 core machining modes in detail (one H3 for each mode)
1. Turning - the king of rotating body parts
Features: Workpiece rotation, tool feeding. Expertise in external round, bore, end face, thread.
Accuracy and surface roughness range.
(Core: explain clearly its characteristics and applications)
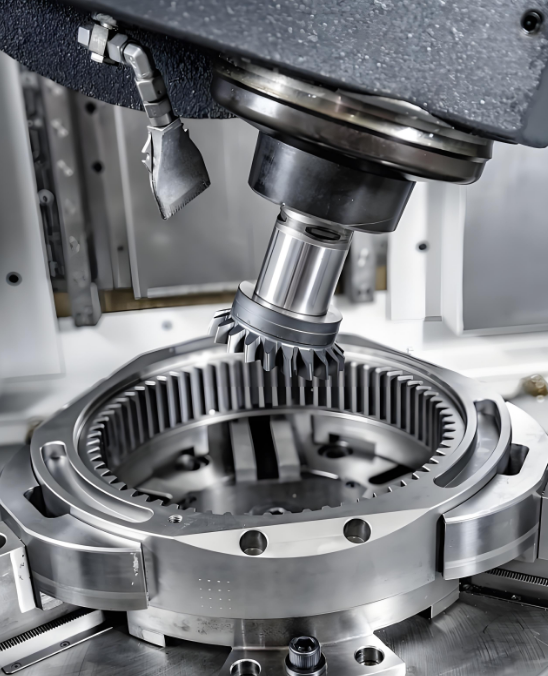
2. Milling - versatile in complex contours and planes
Features: Tool rotation, workpiece feeding. Expertise in flat surfaces, grooves, gears, 3D surfaces.
(Vertical and horizontal milling machines, CNC machining centres)
3. Drilling and Boring - Holemaking Specialist
Drilling: Machining new holes with relatively low accuracy.
Boring: Enlargement and finishing of existing holes to a high degree of accuracy.
4. Grinding - the ultimate in precision and finish
Characteristics: Micro cutting with grinding wheel, used for finishing hard materials after quenching.
5. Wire Excision (WEDM) - for hard materials and complex moulds
Characteristics: Non-contact, using electric spark erosion. Conductive super-hard materials can be processed without cutting force.
6. Laser cutting - efficient and accurate sheet metal cutting solutions
Features: non-contact, thermal processing. Fast speed, good quality cutting surface, suitable for thin plate.
III. Process Comparison and Selection Quick Reference Table
(Design a comparison table listing: process name, primary motion, typical accuracy, surface quality, specialised features, limitations)
IV. Modern Trends: Composite Processing and Intelligence
(Briefly describe the advantages of mill-turn and multi-axis machining centres)
CONCLUSION & CTA: Mastering the characteristics of these processes is a prerequisite for understanding high quality machining. True quality assurance comes from rigorous standards and specifications for machining processes (link to articles IV/V/VI).
FAQ.
“Which method does CNC machining fall under?” (A: CNC is a control method, not a specific process. It can control lathes (CNC turning), milling machines (machining centres), grinding machines, etc., to achieve automation and high precision in many of the above machining methods.)
“What is the difference in way selection between machining aluminium and steel parts?” (A: The basic process is the same, but there are significant differences in cutting parameters, tool materials and coolant selection.)










No comments