Welding is a common method of joining structural steelwork, and for some critical welds, full penetration welding is usually used. When the metal is welded, it is locally heated and melted, and there is a large difference in temperature between the metal in the heated area and the surrounding base metal, resulting in transient stresses during the welding process.
After cooling to the original temperature, the tensile stresses in the weld seam and near seam area and the compressive stresses in the base material are balanced over the entire joint area, resulting in weld residual stresses in the structure itself.
At this time, under the action of welding stress, the structure of the welded part appears to have various types of deformation. The existence of residual stresses and the generation of deformation are mutually transformed, and it is not easy to find ways to prevent, reduce and correct deformation by clarifying the pattern of deformation.
I. Welding deformation of the form and causes
The deformations that occur after welding of steel structures can be broadly classified into two situations, i.e. deformations of the structure as a whole and deformations of the structure at localised locations. The deformation of the overall structure covers the longitudinal and transverse shortening of the structure, as well as bending, that is, warping. Local deformations include convex, wavy and angular deformations.
1.1 Common basic forms of deformation
Plate bevel butt welding, there will be a shortening of the length, that is, the longitudinal contraction of this situation, there will also be a narrowing of the width, that is, the transverse contraction of the kind of deformation, and they, as well as plate bevel butt welding after the angular deformation, which is a common welding deformation of the basic forms of the specific will be the following kinds.
Angular deformation occurs in the member after welding, with different values along the longitudinal axis of the member, and there is an inconsistency in the longitudinal shrinkage of the member flanges and the web, resulting in torsional deformation.
After welding of thin plates, the area of compressive stress on the base material is destabilised, resulting in warping of the plate surface and wave deformation; the longitudinal contraction and transverse contraction of the weld seam is asymmetric with respect to the centre and axis of the member, which triggers the overall bending of the member, and such deformation is bending deformation.
These deformations belong to the basic forms of deformation, and a variety of complex structural deformations are the development of these basic deformations, the transformation of these basic deformations, and the synthesis of these basic deformations.
1.2 Causes of welding deformation
During the welding process, the weldment is heated locally and unevenly, which is the cause of welding stresses and deformations. During the welding process, the metal in the weld seam and in the heated area adjacent to the seam expands, and since the surrounding colder metal blocks this expansion, compressive stresses and plastic shrinkage deformations occur within the weld area, resulting in varying degrees of transverse and longitudinal shrinkage. As a result of the contraction in both directions, a variety of deformations occur in the welded structure.
II. Factors affecting the deformation of welded structures
Because of the number of factors affecting the amount of welding deformation, so sometimes the same factor corresponds to the longitudinal deformation, transverse deformation and angular deformation will show the opposite effect. To comprehensively analyse the impact of various factors for various deformations, to master its influence on the law, which is to take reasonable measures to control the deformation to achieve the desired results of the basis. Otherwise, it is difficult to achieve the desired results.
(1) weld cross-sectional area has an impact, weld cross-sectional area refers to the fusion line within the range of a metal space area, weld area once the larger, the cooling contraction caused by the plastic deformation of the amount will be larger.
(2) welding heat input how to bring the impact: usually, if the heat input is large, then the range of high-temperature zone will be heated, the cooling rate will be slow, and then let the joint plastic deformation zone increases, whether it is for the longitudinal, transverse, or angular deformation, will make the deformation increase the role of. However, when surface cladding, when the heat input increases to a certain extent, because the entire plate thickness temperature tends to be close, so even if the heat input continues to increase, the angular deformation will not increase, but will be reduced.
Preheating of the work, the effect of interlayer temperature, the higher the preheating temperature, which is equivalent to the increase in heat input, resulting in a slowdown in the cooling rate, shrinkage and deformation increase, the higher the interlayer temperature, the same.
(4) the impact of the welding method: in the construction of steel structure welding will often be used in many methods, excluding the case of electroslag welding, submerged arc welding heat input is the largest presence, such as the weld area and other conditions of the same condition, shrinkage deformation is the largest performance. The heat input of manual arc welding is in the middle of the range, and the shrinkage deformation is smaller compared to submerged arc welding, while the heat input of CO2 gas shielded welding is the smallest, and the response of shrinkage deformation is also the smallest.
(5) Effect of weld position on deformation: Given the asymmetrical position of the weld in the structure, such a situation will lead to a variety of deformations.
(6) the rigidity of the structure of the welding deformation will have an impact on the size of the rigidity of the structure, mainly by the shape of the structure and the size of its cross-section is determined by the rigidity of the structure is relatively small, the deformation of the weld will be relatively large, the rigidity of the structure, the deformation of the weld after the completion of the relatively small.
Due to the differences in the assembly methods used, this can have an effect on the deformation of the structure, which is the effect of the assembly and welding specifications on the welding deformation, which is usually less than the deformation that occurs when welding is done after the whole assembly is completed.
In the project welding time, in view of the various conditions and many factors play a role, welding residual deformation presented by the law is relatively complex, know each factor alone play a role in bringing about the impact of the project will help to carry out specific comprehensive analysis of the specific situation.
III. Measures to prevent and reduce structural deformation
One, reduce the cross-sectional area of the weld, two, under the prerequisite of obtaining an intact weld free of excessive defects, three, go for the smallest possible bevel size, and four, this bevel size includes the angle as well as the gap, period.
Second, for the yield strength is below it, the hardenability is not very strong steel, using relatively small heat input situation, as far as possible not to preheat or moderate reduction of preheating temperature and interlayer temperature; give priority to selecting the smaller heat input welding method, such as CO2 gas shielded welding method.
(3) thick plate welding as far as possible using multi-layer welding instead of single-layer welding.
(4) When both sides can be welded operation na, have to use both sides of the symmetrical bevel, and in the multi-layer welding to be used and the component and the axis of symmetry of the welding sequence, as shown in Figure 2, below.
Figure 2: Reduction of angular distortion with symmetrical welding sequence with double-sided bevelling
(5) T-joint plate thickness is larger with open bevelled corner butt weld, see Figure 3:
Figure 3: Open bevelled fillet butt weld for large plate thickness of T-joints
(6) The use of pre-welding anti-deformation method to control post-welding angular deformation, which is extremely common in the production of a method to pre-welded parts to the basic offset (compensation).
The purpose of preventing deformation after welding is achieved by means of a counter-deformation method that presents a curved state after welding. Table 1 and Fig. 4 show the reference values for counter-deformation of box columns before welding and H-beams before welding, respectively:
![图片[1]-一、焊接变形的形式与原因-大连富泓机械有限公司](https://cndlfh.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/12/QQ20251002-201911.png)
Fig. 4 Reference value of back-deformation of H-shaped steel flange before welding
(7) Rigid fixation method, also known as forced method. In practice, the post-welding distortion is usually less for components with high rigidity. In the case of less rigid members, the rigidity of the member can be increased before welding, so that the post-weld deformation will also be reduced. When applying this method, it is important to wait until the weld has cooled down before removing the fixtures and supports. Several common methods include the fixture method, the support method, the tyre method, the temporary fixation method (such as the nail fixation and the compression fixation method), and the tack welding method.
(8) hammer weld method: this method is mainly applicable to thin plate welding, when the weld of the thin plate and its heat-affected zone is not yet in a completely cooled state, to immediately hammer for that area, for thick plate is the use of wind gun to hammer.
(9) Compensation of longitudinal shrinkage deformation of the weld seam by the method of reserving the length of the member.
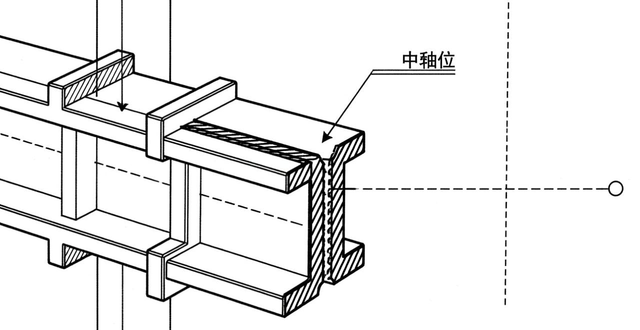
(10) When designing, it is necessary to reduce the number and size of weld seams as much as possible; to arrange the weld seams rationally, in addition to preventing the weld seams from appearing dense, it is also necessary to position the weld seams as close as possible to the centre and axis of the member, and to make the weld seams as close as possible to the member's .
Symmetrical to the shaft.
(11) The welding sequence should be correctly selected. When there are butt welds and fillet welds in the steel structure, the butt welds should be welded first and then the fillet welds should be welded in the opposite direction according to the principle; for the cruciform welds and T-shaped welds, the correct sequence should be adopted to avoid the concentration of the welding stress, so as to ensure the quality of the joints; the welding method of welding symmetrically in the centre and shafts of the steel structure, and the welding method of welding from the middle to the two sections are very beneficial to the reduction of deformation. Adopt the welding method which is symmetrical to the whole steel structure and the axis, and adopt the welding method from the middle to the two sections, which is very favourable to reduce the deformation, and when welding the important parts of the steel structure with high strength requirements, the joints should be allowed to contract freely without constraints as far as possible.
Four, welding deformation of the post-weld correction method
In order to meet the design, specification requirements, welding deformation of welded structural components have to be corrected, put it another way, this correction is actually trying to find ways to create new deformation to compensate for or offset the deformation that has occurred. Construction production, the most commonly used post-weld residual deformation correction method can be divided into force correction, heating correction and the combination of these two methods used in these cases.
4.1 Force correction method
Straightening operations are usually carried out with the aid of a jack, or by means of a screw loader, or by means of a roller straightening machine, or by means of a large press.
4.2 Heating correction method
This means that by means of uneven heating, the structure acquires a reverse deformation, which is intended to compensate for or counteract the original weld distortion. The heating method of heat correction can be divided into point heating, line heating and triangular heating. Heating correction can eliminate many force correction can not deal with the deformation, control the flame local heating caused by the deformation of the law is to do a good job of correction of the focus, to determine the effect of flame correction is mainly the location of the heating and heating temperature. Mild steel and common alloy welded structures are usually used 650 to 8000C heating temperature, generally not suitable for more than 9000C. see table 2 various colours can distinguish the temperature range.

When correcting with the help of heating, in order to make the correction effect can be improved, then in the heating process can also apply external force to correct, when the flame correction, the cooling of the heating point exists in two ways, that is, natural cooling and water cooling, the use of water and fire correction method can make the structural correction to harvest faster results, and can make the correction amount exceeds the natural cooling correction amount, like correcting the large cross-section of H steel sections.




















No comments